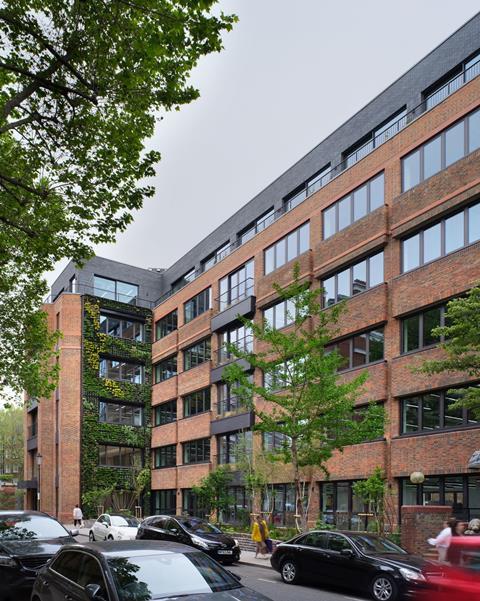
Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole council has built an education centre from timber groynes reclaimed from the beach in an attempt to reduce the 2,000 tonnes of waste left behind on the sands each year. Thomas Lane looks at the project, which has been shortlisted for the net zero award at this year’s Building Awards

Each year, some seven million people visit the golden sands of Bournemouth, an 11-mile beach stretching from Bournemouth in the middle to Sandbanks in the west and Christchurch to the east. Collectively, these visitors leave 2,000 tonnes of rubbish behind, which is removed and processed by Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Council at a cost of £1m.
Most of this rubbish is deposited in beachside waste bins, but sadly not all. The council has a dedicated site at Durley Chine beach to deal with up to 500 tonnes of litter left on the sands, which consumes half of the £1m budget. This facility has a dedicated team of staff to operate a fleet of tractors armed with special scoops to sift the rubbish out of the sand and pack it into containers ready for shipping out.

The cost and environmental impact of this waste prompted BCP council to commission a report called Turning the Tide, which recommended how to reduce the amount of single-use plastic on the beach. This includes providing free water bottle top-up stations along the beach and reducing single-use plastic use in beachside catering facilities run by the council.
The biggest element in this waste reduction strategy is a new environmental hub built next to the beachside waste site. Called the Durley Chine Environmental Hub, it integrates five functions and has been shortlisted in the net zero category at the Building Awards 2023.
These include better quality welfare facilities for waste site staff, two meeting rooms for use by visiting schools and the community, a kiosk selling drinks and snacks, new toilets and an area for an exhibition to educate people about waste and recycling. Given its function, the building needed to be a sustainability exemplar, too.
“The specification for the project was to provide a very sustainable building, focusing on the environmental aspects, not only of the building, but also how it was going to be used in future,” explains Zoe James, BCP council’s project manager.
As the building would not generate enough revenue to cover its £2.4m construction cost, the council had to seek external funding. It drew up a rough “guide” scheme which included floor areas for each of the functions for a funding bid to the Coastal Community Fund. This was successful.
Armed with this rough guide, the council went to multi-disciplinary consultant WSP, which is on its consultants framework, and Footprint Architects to turn the guide scheme into a project that would meet the council’s aspirations.

Peter Ward, the founder of Footprint Architects, explains that each of the five elements was carefully considered in terms of its function and the environmental strategy. “We split the building down into its functions and then created a bespoke environmental strategy for each one of those pods to enable us to reduce the heating requirements and reduce carbon,” he says.
The welfare facilities and meeting rooms are housed in a two-storey block on the east side of the scheme with the toilets and kiosk on the west side. The exhibition space is sandwiched in the middle and is open.
Building Awards 2023
The Durley Chine project has been shortlisted in the net zero category at this year’s Building Awards.

The Building Awards recognise and celebrate the very best in your industry and provide an opportunity to enjoy yourself among the industry’s best and brightest.
This year’s ceremony will take place on 7 November at Grosvenor House Hotel and tickets are selling quickly.
Secure your place today at building-awards.com
“An open space for the visitor centre is likely to be more appealing and bring people in than one with doors,” Ward says. These disparate elements are united by a green roof covering the two-storey block, the exhibition space and kiosk with the toilets left as a freestanding unit.
Ben Moss, director of building structures at WSP, says involvement right at the beginning of the project was a bonus as it enabled the team to thoroughly appraise the energy use and embodied carbon impacts of a range of options. “We even queried whether we needed foundations,” Moss says. “We went through the analysis and concluded that, in this location, foundations were a good idea.”
He says that BREEAM was not appropriate for this project, but building to Passivhaus standards would reduce energy use in the welfare and meeting room block. But Passivhaus was not extended to the toilets and kiosk because the extra insulation needed to meet the standard would increase the embodied carbon without reducing operational carbon. This is because the kiosk window is open all day and the toilet doors are constantly opening and closing.

The toilet and kiosk walls are built from concrete. Moss says the original aspiration was to use rammed earth, but this was deemed unsuitable for the harsh beachside environment.
“What we wanted was a building that feels very contextual and weathered with its surroundings,” Ward says, adding that he wanted the kiosk and toilet walls to reflect the sand of the beach and strata of the cliffs. This has been achieved using several layers of concrete made from different sizes and colours of sand and aggregate.
The use of concrete sounds counter-intuitive in terms of embodied carbon, but Moss says the analysis shows otherwise. The single-storey walls carry relatively small loads so did not need any reinforcement.
The cement content of the mix was reduced by 30% because a strong concrete was not necessary for strength or reinforcement protection. Furthermore, 80% of the cement content has been replaced by GGBS. The wall is slightly thicker to compensate for the lack of reinforcement.
“We cross-checked against what the embodied carbon would have been if we had gone for a thin reinforced concrete wall and concluded that we had indeed saved some carbon,” Moss says.

What is unique about this job is the extensive use of reclaimed timber. The building includes 45 tonnes of wood reclaimed from the groynes – shore protection structures – on the beach. There is a further seven tonnes of wood reclaimed from a naval yard in Germany.
The timber has been used for the secondary roof structure, brise soleil, cladding and the decking. Getting to this point has taken a lot of hard work and determination because reusing timber is much more involved than reusing steel, which is a more predictable and easily assessed material.

Moss spotted a stockpile of suitable timber while out on a run. “I live locally and was out for a run one day and found this massive stockpile of timber in the Solent Beach carpark that the council had extracted from the groynes,” he says.
The groynes are replaced every 25-35 years and the council is also going through a process of realigning the groynes along the entire seafront as part of a 100-year project to provide more effective beach protection. The groynes are constructed from a combination of greenheart and ekki, which are both durable tropical hardwoods suitable for marine applications.
Each groyne consists of posts which go down up to 7m into the sand, and planks fixed between the posts. Some of the timber is reused for other projects but not all – Moss says there was plenty of leftover timber suitable for the environmental hub.
Once the flood and coastal risk management team, who are the custodians of the timber, had been persuaded to part with some of it, the timber had to be checked to see if it was indeed suitable for a building. “From the section size point of view, it looked suitable and it’s tropical hardwood, mostly greenheart, so we knew it was going to be pretty strong,” Moss says. “But then you have to start researching how you actually go about it. For example, how do you check that it really is greenheart?”
Moss brought Phil O’Leary, technical manager of Trada, which specialises in timber testing, certification and consultancy to assess the old groynes. “Phil gave us a bit of a conundrum because he said we couldn’t just say, because that was greenheart grade D70 20 years ago, it still is.
“It has to be regraded in the finished section size, so there is the risk of machining a whole load of timber to the right size and then finding out that it doesn’t meet the grading requirements and has to go in the skip.”
Building in a factor of safety by over-specifying the section size was considered then discounted because of the variability of the timber. “You can’t simply add a factor of safety and deliberately over-design because, if there’s a big knot or a crack, that might reduce the usefulness of the section from 100% to 0%,” Moss says. “With steel, generally we have a pretty good idea of provenance and it’s relatively easy to test.”
The answer was to do a quick initial grading. For example, knots have a bigger impact on the integrity of the timber than a hole of the same size. Moss adds that there is also a risk of weathered timber bending in one direction after it has been machined because of the difference in weathering on either side.
Timber with potential was machined to size. Machining was kept to a minimum to ensure the section sizes were as close as possible to the original. The design had to be tweaked to suit the available section sizes.

Finding someone to machine the timber also proved to be a challenge because of the size and density of the wood plus the risk of hidden nails damaging saws. A sawmill called East Bros Timber in Salisbury, which the council had used previously, was happy to take the job on.
Having got this far, the council wanted to know how long the timber would last once it was integrated into a building. “The answer is we don’t know, because there is no way of knowing how much of the inherent preservative qualities, the natural oils and so on have been leached out in over 20 years in the sea,” Moss says.
Unable to provide certainty, a decision was made to use new timber for the primary structure. “That’s why we’ve gone with new FSC-certified timbers for the key structural elements,” explains James. “Otherwise, we could have had issues when trying to get insurance.
“We were very comfortable with how the reclaimed timber has been used, but we did have to have those initial discussions about how to use the reclaimed timber safely.”

The reclaimed timber has been used for areas where it can be easily replaced: the cladding, brise soleil, and areas where the wood will be protected from the weather such as the secondary roof structure. As greenheart is toxic and people are likely to walk into the visitor centre barefoot, the risk from splinters was deemed too high. So the reclaimed timber from Germany was used for the decking.
Moss says this project was only possible because of WSP’s early involvement in the design and the fact that the building was constructed by the council’s in-house contractor. “If we had had a traditional contractual arrangement, some of these things wouldn’t have happened because someone would have said this wasn’t in their scope or wasn’t what they priced for. We would have fallen foul of the ’it’s easier just to do it the way we always do it’ mindset,” he says.
The council’s contracting team’s positive mindset also helped. “The team were very enthusiastic about the building. It challenged but also really interested them as well, so they took on ownership,” James says. “The site manager, who is a chippy by background, was very into sorting out the detail – which was a real benefit.”
The finished structure will be net zero in operation as the roof-mounted PV panels provide enough power to heat, light and ventilate the building. The reclaimed timber and a general focus on reducing the carbon impact of all materials – such as newspaper-based insulation for the walls and recycled plastic splashbacks in the toilets – add up to an upfront embodied carbon figure of 172kg of carbon dioxide per square metre including the exhibition space. This smashes the LETI 2030 upfront embodied carbon target of less than 300kgCO2/m2 for an education building, making it an A+ rating building for upfront carbon.

The building also looks great. The reclaimed timber cladding and layered concrete walls of the kiosk and toilets are very much of the beachside location, making it seem as if the building has always been there rather than recently finished.
The bonus of this approach is that the exterior should be virtually maintenance-free and durable, unlike other buildings on the beach front which suffer from saltwater-laden winds. Some relatively recent buildings have been demolished because saltwater has percolated through cracks in the walls and corroded the reinforcement.
Would the team use reclaimed timber for a construction project again? Moss offers a cautious yes, but says it is very project specific.
“We did have a nice alignment of those factors, which you won’t necessarily get on other projects,” he says. “You need this coincidence of circumstances where the project suits the supply of timber and the aesthetic too. We had a project where slightly ropey timber was what we wanted, so it all hangs together.”
He adds that regulation or cost savings would be needed to drive more widespread use of reclaimed timber. “If there is enough of a cost saving by reusing timber, then it will find its own way into the market – or, if regulation starts dictating it, then it will have to be done. But, compared to other building materials, timber is already a low-carbon material and therefore the incentive for people to use it isn’t that great.”

BCP council is in a good position to continue using reclaimed timber on future projects as it has a ready supply of high-quality durable wood, and a favourable supply chain arrangement. James thinks the reclaimed timber may have been cheaper than new as it did not cost anything, although the machining was expensive. The council is yet to do the sums.
James’s colleague, Andrew Brown, the council’s seafront operations manager, strikes a positive note. “The plan for this site is part of a much broader development plan for the seafront. So could reclaimed timber be used elsewhere? Yes.
“Some of those projects may come forward in the next few years subject to funding opportunities. And we may be in a similar situation; where timber is still being pulled out of the sea every year, it can be recycled and repurposed for those future projects.”
Brown adds that some reclaimed scaffolding boards were recently used on another kiosk further along the beach. Indeed all the signs are that the environmental hub has already proved to be a positive catalyst for change.
Project team
Client and project manager BCP Council
Architect Footprint Architects
MEP and structural engineer WSP
QS Peter Gunning and Partners
Employers agent Frazer Garner Associates
Passivhaus consultant Warm Consulting
Contractor BCP Council Construction Works Team
MEP specialist Spectrum Electrical Group
2023 Building Awards: The Net Zero Award shortlist
The Durley Chine Environmental Hub was shortlisted for Building’s Net Zero Award, in partnership with UKGBC. Read on to find out more about the other nine contenders for the award.
The 2023 Building Awards are being held at Grosvenor House Hotel in London on 7 November. Click here to buy your ticket.
Halifax Trinity Road Ground Source Heat Pump: Lloyds Banking Group
How do you decarbonise an inefficient grade II listed office without negatively affecting the building’s appearance or disrupting staff? The Halifax head office is an iconic 1970s building in the Yorkshire town which is heated by three ancient 2,200kW boilers dating back to the building’s opening. The building guzzles over 20,000MWh of gas and electricity annually, more than any other building in the bank’s 1,400 strong estate and is responsible for a staggering 10% of its entire gas consumption.
The building is located over an old brewery and, working with Mitie, three historic boreholes were identified for use with an open source heat pump. The project met several hurdles including the need for two new 300m deep boreholes because the originals were not viable.
The new arrangement did not have the capacity to meet all the building’s needs, so a 50,000 litre storage tank has been installed as a heat reservoir for use at peak times. The £4.7m project will meet 97% of the building’s annual heating load and save over 1,100 tonnes of CO2 a year.
Retrofit Accelerator – Homes Innovation Partnership: Mayor of London
This partnership brings together housing associations and suppliers of innovative offsite manufactured retrofit solutions for upgrading social housing with minimum resident disruption. Solutions include the Ultrapanel Housewrap kit of parts, the BowTie Ventbox ventilation system, which includes 3D printed ductwork and Monodraft’s energy pod.
Suppliers develop the solutions, which are prototyped and piloted before being rolled out at scale. The partnership to date includes nine housing associations and four suppliers who are currently working on 100 retrofits.
The plan is to launch a framework with a potential value of up to £10bn for retrofitting 190,000 homes and providing 150,000 jobs over 10 years. The framework will be open to social housing providers across the UK and could make a significant contribution towards tackling carbon emissions from homes.

Ultra-low carbon reusable steel: EMR
Reusable steel is in vogue with developers as it is a good way of reducing carbon emissions from new buildings. Scrap-metal specialist EMR has helped kickstart this trend by establishing a supply chain for reclaimed steel.
Working with demolition contractors, EMR takes steel from demolished buildings and tests the metal to establish its properties. It pays a premium for reclaimed sections to incentivise demolition contractors to recover the steel and cover their additional costs. Suitable steel is cleaned up and prepared for reuse.
EMR has achieved an Environmental Product Declaration for its steel sections of 46.6kgCO2/tonne, which it says is a 97% reduction compared with a new steel section. The company says it is in the process of supplying over 400 tonnes of steel to several major London schemes over the next few months.

Holbein Gardens: Barr Gazetas
Rather than redeveloping a tired, 1980s office building next to Sloane Square tube station, developer Grosvenor worked with architect Barr Gazetas to refurbish the building instead.
The building has been fitted with new energy-efficient windows and extended upwards using reclaimed steel sections for the new structure. Elsewhere embodied carbon has been reduced by using reclaimed raised access flooring and bricks which are jointed with lime mortar to facilitate future dismantling.
Biodiversity has been increased with green walls and a green roof with new landscaping at ground level. Targeting BREEAM Outstanding and LEED Platinum, the building is now all-electric, with a predicted 69% reduction in energy use compared with a traditional office building.
The project has achieved an upfront embodied carbon figure of 298kgCO2/m2, which comfortably beats the LETI 2030 target of 350kgCO2/m2.

University of Salford Energy House 2.0: Aecom
At first sight the Energy House 2.0 looks like any other industrial shed; it is the contents that mark this project out. Energy House 2.0 provides a controlled environment for the performance testing of full-sized houses and the services within those homes. Capable of testing two houses in two separate chambers, these can be subjected to temperatures ranging from -20°C to +40°C.
Wind, rain and snow can be simulated; the building features a giant pit so even the earth the homes sit on can be changed to test the impact of different ground conditions.
The building itself has impressive sustainability credentials, achieving a BREEAM Excellent and an EPC A rating. The building enables empirical, repeatable testing of a range of building systems and should help to define the most effective low carbon solutions for new build housing.
The Embodied Carbon Calculator: Turner & Townsend
The ability to calculate the embodied carbon in a proposed scheme is becoming a necessity for most firms. What makes this tool special is its ability to calculate embodied carbon and cost so cost managers can quickly identify the financial implications of a range of different construction options.
It has been designed to be simple to use, enabling the firm’s 400 cost managers to use it as a day-to-day tool throughout the project lifecycle, enabling them to provide clients with the most cost effective, low carbon solutions. The tool is aligned with RICS new rules of measurement 1 and RICS whole life carbon assessment guide to provide industry standard calculations. The company says the tool can be easily updated to take account of new industry cost and carbon calculation methodologies.
The tool has been used on live projects including at Exeter University, where the cost and embodied carbon impact of new development was compared to decarbonising existing buildings. The tool helped to establish that refurbishment would offer a 50% reduction in embodied carbon.

The Entopia building: ISG
When the Institute for Sustainability Leadership at Cambridge University decided it wanted a new HQ, it had to be an exemplar for low carbon construction. Located in an old telephone exchange that had already been converted into an office, this deep green refurbishment features 35% bio-based materials including wood fibre insulation, lime and cork plaster and a cellulose based acoustic coating applied to the soffits.
The building is targeting BREEAM Outstanding and has already met the EnerPhit standard with a predicted operational energy use of 58kW/m2/yr. Monitoring suggests the building is beating this target with actual energy use of 45 kW/m2/yr.
Reclaimed raised access flooring and 350 reclaimed LED light fittings from a London office have helped to keep embodied carbon to a minimum. Reclaimed steel was used for the structure of the roof-top PV array and the original carpet tiles were kept, cleaned and reused for 12% of the building’s floor area.
The result is an upfront embodied carbon figure of just 130kg/CO2/m2 with whole life carbon calculated at 409kgCO2/m2 over 100 years. This project is an exemplar with valuable lessons for anyone taking on a low carbon office refurbishment.

11 & 12 Wellington Place: Wates
This office development in Leeds is the first project outside London to receive a NABERS 5* design review rating. It also boasts a BREEAM Outstanding rating, an EPC A and satisfies the UKGBC’s criteria for a net zero office.
The triple-glazed, all-electric building achieved an impressive airtightness rating of 1.47m3 hr/m2@50pa and is targeting a 41% reduction in operational energy use which is aided by a 700m2 roof-mounted PV array, saving 407 tonnes of CO2 a year.
Contractor Wates mitigated construction emissions by fitting 36 PV panels to its site cabins, which reduced energy use by 26%. Wates also helped the project to achieve a LETI target beating upfront embodied carbon figure of 532kgCO2/m2 with methods including using thermal lightweight aggregate screed rather than traditional sand and cement and sending over 24,000m2 of floor protection back for remanufacturing.

Eliminating wasted energy in buildings: Measurable Energy
The Measurable Energy smart socket is a good example of a small intervention with a potentially big impact. The socket starts monitoring a device’s energy use after it is plugged in and uses machine learning to establish its power use routine. Once learnt, the socket automatically switches the device off outside the times that it is needed.
The socket also features a traffic light LED indicator which utilises a link to the National Grid to glow green when power is mainly coming from renewable sources, orange when mixed renewables and fossil fuels are providing power and red for fossil fuels. Power consumption data can be viewed on a dashboard.
The device is being used by companies including Balfour Beatty, the Francis Crick Institute and Reading University. Kier trialled 34 of the sockets on two site cabins and reported a 59% energy use saving.
Interventions it tried included setting up a link to the Met Office that enabled a dehumidifier to be turned off when the weather was dry.

























No comments yet